
Clotting products such as kinins and thrombin also enhance capillary permeability. This process causes edema, which has 2 phases: in the initial phase, edema will occur immediately after the secretion of histamine and leukotrienes from mast cell which cause vasodilation. Afterwards, the wound-surrounding tissues and capillary endothelial cells will secrete the histamines which permeate the capillary wall and increase the interstitial space, resulting in fluid flows from the capillaries to the interstitial space. Specific enzymes are secreted from the cell membrane to stimulate prostaglandins and leukotrienes synthesis. After blocking the bleeding wound, the aggregated platelets will secrete a chemo-attractant to activate the inflamed cells in order to start the wound-healing process.
#Turf burn healing process skin#
This phase occurs within 24 hours after the skin is injured and continues for several days or weeks depending on the level of the injury. It is not only the platelet release clotting factor that is involved here they also provide cytokine and growth factors such as Platelet-Derived Growth factor (PDGF), Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β), Insulin-like growth factor-1, and platelet factor-IV, which facilitate the wound-healing process.
Then, prothrombin is triggered to be assembled as thrombin as with fibrinogen, which is transformed to fibrin to stop the bleeding at the wound site. Afterwards, platelet aggregation will emerge, accompanied with the release of some clotting factors from the cells which stimulate the coagulation and complement cascades through intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways. Skin injury can cause vasoconstriction, which occurs immediately in order to stop the bleeding. Wound healing has four phases: hemostasis, inflammation, tissue proliferation and tissue maturation or remodeling that overlap in time (Figure 1).

Wound-healing process Wound healing is the process of healing after physical tissue injury and this process involves soluble mediators such as cytokine or growth factor, blood cells such as platelets and white blood cells, extracellular matrix, and parenchymal cells.

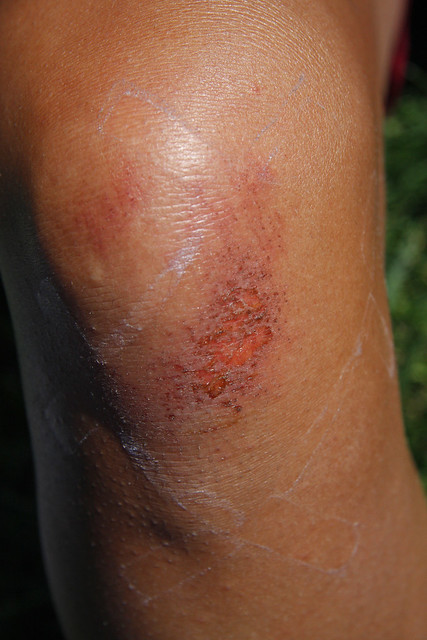
There are various types of wounds, including an incised wound, a lacerated wound, abrasions, contusions, ulcers, and burn wounds.
#Turf burn healing process update#
This review presents the pathophysiology of burn injury, and provides an update on current management of burn wound care.Ī wound is an injury to a part of the body, especially one in which a break is made in the skin or tissue. Aburn wound is a type of skin injury caused by tissue damage after exposure to heat fire, flame or scalds, chemicals, electrical, or radiation.1 Burn causes an estimated 300,000 deaths yearly worldwide and may occur in any age group or sex and in both developing and developed countries.2 If healthcare providers understand the pathophysiology of burn injury, evaluation levels of burn, early resuscitation and good management, this can help to decrease the incidence of burn mortality and mobility.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
